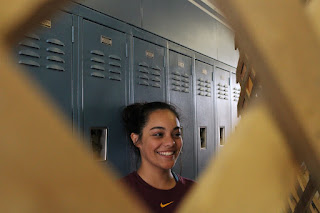Framing
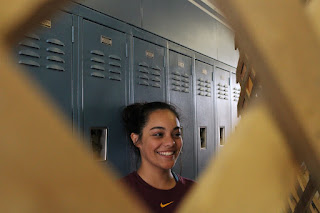
1) I used framing in this photo.
2) The subject in this photo is Julianna, specifically her face.
3) Yes it is clear what the subject is.
Avoiding Mergers

1) I used the rule avoiding mergers in this photo.
2) The subject in this photo is Riley.
3) I think that the subject is somewhat clear.
4) I could have focused the camera a bit more on her.
Lines

1) I used the rule lines in this photo.
2) The subject in this photo is the drying rack lines.
3) I think the subject is clear because the camera is focused on the leading lines.
Simplicity

1) i used the photo rule of simplicity for this picture.
2) The subject in this photo is the word paint.
3) I think that the subject is clear in this photo since the frame is filled with the subject (paint).
Rule of Thirds

1) I used the photo rule rule of thirds.
2) The subject on this photo is Julianna.
3) I believe the subject is clear in this photo.
Balance

1) I used balance for this picture.
2) The subject in this photo is the balance of the black and red columns.
3) This photo's subject isn't very clear.
4) I could have gotten a picture more focused on one subject.